Troubleshooting Steam: How to Resolve Games Not Showing Up
Encountering the problem of Steam not recognizing your installed games can be incredibly frustrating, especially when you’re eager to start playing but your library seems empty or incomplete. This issue is common among gamers and can stem from various causes, including system glitches, file corruption, or misconfigured settings. Fortunately, there are effective solutions to get your games back in sight and running smoothly. Whether you recently moved files, uninstalled games accidentally, or faced a system error, understanding the root causes and remedies can help you quickly resolve the issue and resume your gaming experience.
Before diving into troubleshooting, confirm that your games are indeed installed on your computer. Sometimes, users forget whether they’ve removed or moved certain files, which can cause Steam to lose track of them. To verify, open your Steam library and look for the “Installed” tag at the top of the page. If your game isn’t listed as installed, you might need to reinstall it to restore its visibility in your library. Reinstallation is straightforward but ensures that Steam recognizes the game correctly afterward.
If your games are installed but not appearing in your library, restart Steam. Small glitches or temporary bugs can interfere with the program’s ability to display installed titles. Closing and relaunching Steam often resolves these issues by refreshing the application’s state. Additionally, clearing the download cache can also help, especially if corrupted cache files are causing recognition problems. To do this, navigate to Steam’s settings, click on the “Downloads” tab, and select “Clear Download Cache.” This action forces Steam to rebuild its download history and can resolve discrepancies in game detection.
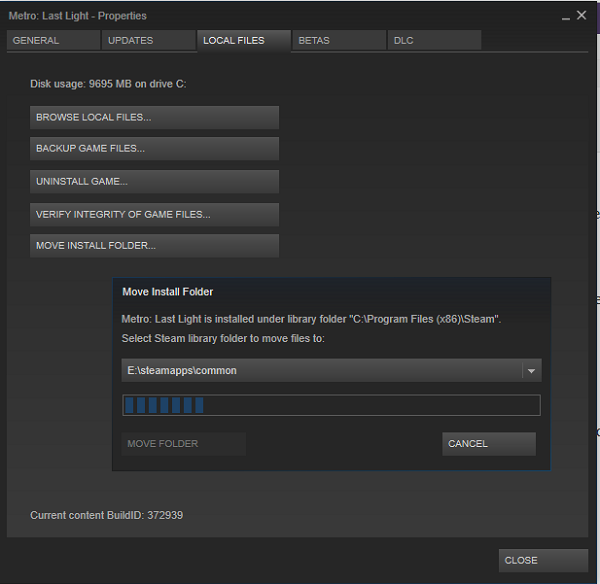
Another potential cause involves issues with Steam’s file system, particularly if game files have been moved manually or become corrupted. Moving game directories outside of Steam’s default folders can lead to recognition issues. To correct this, you should verify the integrity of game files. Right-click on the game in your library, choose “Properties,” then go to the “Local Files” tab and click on “Verify Integrity of Game Files.” Steam will scan the files and replace any corrupted or missing data, ensuring the game appears correctly in your library.
In some cases, outdated or corrupted cache files stored in the Steam directory can prevent games from being recognized. Deleting the “appcache” folder can resolve this problem. To do so, close Steam completely, then navigate to the Steam installation directory (usually at C:Program Files (x86)Steam). Locate and delete the “appcache” folder. When you restart Steam, it will automatically regenerate this folder and update your game listings, often fixing recognition issues caused by outdated cache data.
Understanding the importance of proper setup and maintenance, some developers and service providers emphasize the value of using robust development practices. For instance, scaling your vision with dedicated teams can ensure that your game development projects are well-managed, which indirectly reduces issues like recognition errors in distribution platforms. Additionally, exploring alternative ways to create and manage your gaming library, such as the benefits of cross-platform solutions, can provide more flexibility and stability across different systems.
In conclusion, troubleshooting Steam’s failure to recognize installed games involves verifying installation status, restarting the application, clearing caches, and checking file integrity. These steps are generally quick but crucial for restoring your access to your game library. By following these procedures, you can minimize downtime and get back to enjoying your favorite titles without unnecessary frustration. For more insights into game development and related topics, understanding the role of indie developers can also be beneficial—check out this guide to learn how independent creators contribute to the gaming ecosystem.